How to Tell if Your Bearded Dragon is Male or Female
Whether you're a seasoned herpetologist or a curious newbie, understanding the gender of your bearded dragon is crucial for their care and breeding.
Bearded dragons are among the most popular reptilian pets, known for their docile nature and expressive behaviors. But when it comes to determining their sex, many owners find themselves scratching their heads. Whether you're a seasoned herpetologist or a curious newbie, understanding the gender of your bearded dragon is crucial for their care and breeding. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the steps to identify the sex of your bearded dragon with ease.
Key Takeaways:
- Learn the physical differences between male and female bearded dragons.
- Discover behavioral cues that can indicate the gender of your pet.
- Gain insights into the importance of knowing your bearded dragon's sex for proper care.
Physical Characteristics
It's important to note that differences in physical characteristics become more evident as the bearded dragon reaches sexual maturity, usually around 5-6 months of age.
Hemipenal Bulges
The presence of hemipenal bulges is one of the most reliable methods to determine the sex of a bearded dragon. To check for these bulges, gently lift the dragon's tail and examine the area directly behind the vent. In males, you should see two distinct bulges, one on each side of the tail. This is where the male reproductive organs are housed.
In contrast, a female will typically have a single, central bulge or none at all. This method requires some care, as improper handling can cause stress or injury to your pet. It's best to perform this check when the bearded dragon is relaxed and in a warm environment, as this can make the bulges more visible.
You can also examine the internal sex organs of a beardie by holding up the tail and shining a bright light behind it. If male, you should be able to see two darker spots in the same area at the bulges would be. If female, you might see one, smaller spot, or none at all.
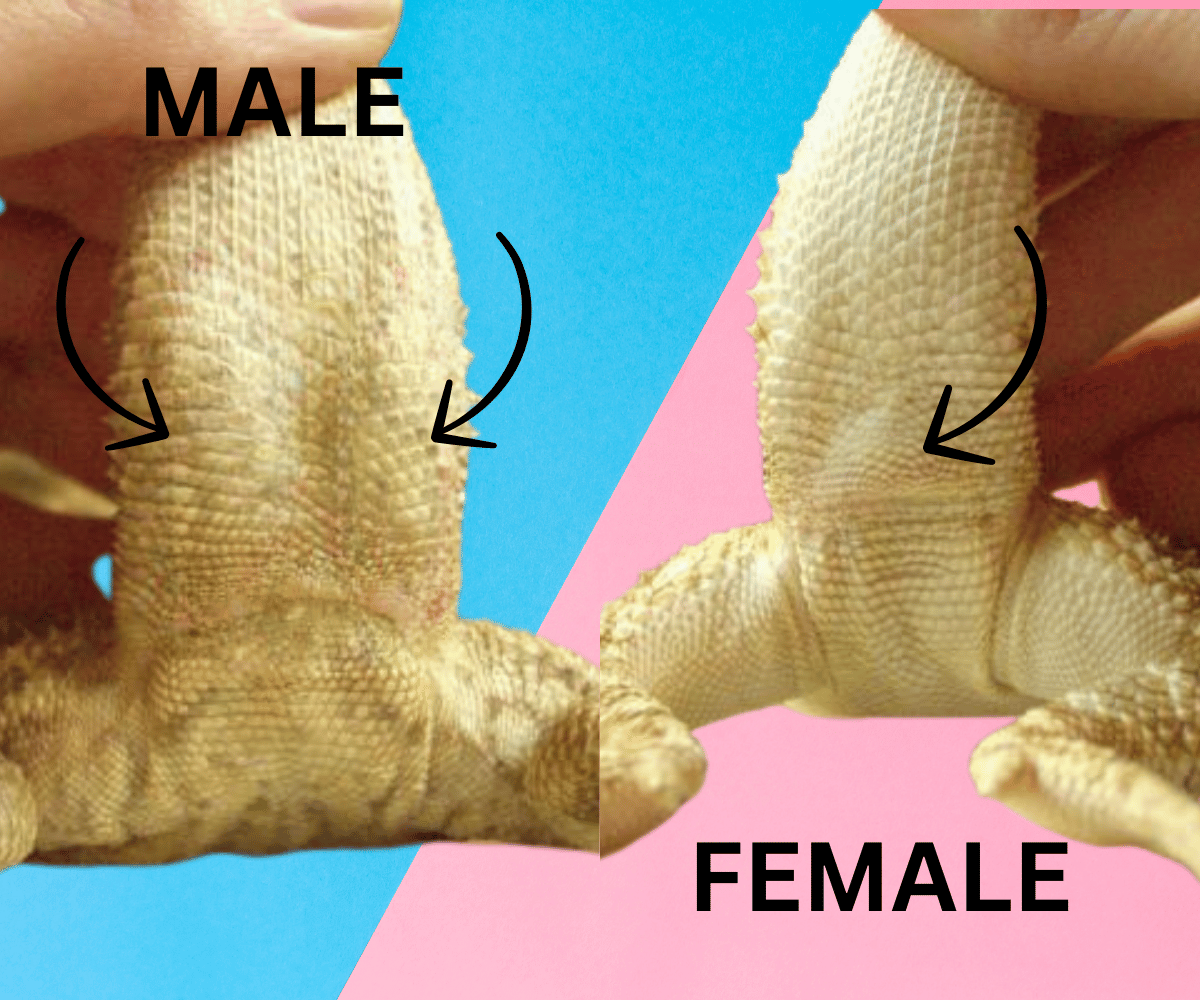
Femoral Pores
Femoral pores are another physical feature that can help identify the sex of your bearded dragon. These pores secrete a waxy substance used in scent marking and are more prominent in males. To inspect the femoral pores, look at the underside of your bearded dragon's hind legs.
In males, these pores are larger and may have a waxy buildup, especially during the breeding season. In females, the pores are smaller and less noticeable. While this method is less invasive than checking for hemipenal bulges, it still requires a keen eye and may not be as definitive in younger dragons.
Head and Tail Structure
The structure of a bearded dragon's head and tail can also give clues to its sex. Males generally have wider, more triangular heads due to larger jaw muscles used in combat and courtship displays. Their tails are thicker because of the hemipenal bulges and tend to remain thick all the way to the tip.
Females have narrower heads and their tails taper more sharply after the vent, lacking the pronounced bulges found in males. These differences can be subtle, especially in younger dragons, but become more apparent as they reach sexual maturity.
Size and Weight
While size and weight can sometimes be indicators of sex, they are not as reliable as other methods. Generally, male bearded dragons can grow larger and weigh more than females. However, this is not a definitive rule, as individual growth can be influenced by factors such as diet, genetics, and overall health.
It's also worth noting that females may appear larger when gravid (carrying eggs), which can be misleading. Therefore, size and weight should be considered alongside other physical and behavioral characteristics when determining the sex of your bearded dragon.
Without a side by side comparison of male and female beardies of the same age, it can be difficult to determine sex using these characteristics.
Behavioral Signs
Behavior can also be a telltale sign of your bearded dragon's sex. Males often exhibit more territorial behaviors, such as head bobbing or arm waving, to assert dominance or attract a mate. They may also become more aggressive during the breeding season. Females, while they can display similar behaviors, typically do so with less frequency and intensity.
Breeding Behaviors
During the breeding season, which typically occurs in the spring and summer, bearded dragons exhibit more pronounced sexual behaviors. Males become more active, displaying head bobbing and arm waving to attract females. They may also become more vocal, making hissing sounds as part of their courtship ritual.
Females ready to mate may respond to a male's display with submissive behaviors, such as head bobbing at a slower pace or flattening their bodies. If you observe these interactions between bearded dragons, it can be a clear indication of their respective sexes.
Nesting Behaviors
In addition to these displays, females may show signs of nesting behavior when they are ready to lay eggs, even if they have not been with a male. These include persistent digging, particularly in one area of the enclosure, and the creation of a burrow-like structure. Additionally, the female may become more territorial and protective of her chosen nesting site. Observing these behaviors alongside physical characteristics can provide a clearer picture of your bearded dragon's gender.
Age and Sexual Maturity: Timing is Key
Age plays a significant role in determining the sex of a bearded dragon, as many sexual characteristics are not visible until they reach maturity. Bearded dragons typically reach sexual maturity around 8 to 12 months of age, although this can vary.
Before this age, it can be challenging to accurately determine the sex of a bearded dragon due to the lack of developed sexual dimorphism. Patience is essential, and it's often best to wait until they are fully mature to make a definitive assessment.
Expert Consultation: When to Seek Help
If you're having difficulty determining the sex of your bearded dragon, or if you're unsure about handling them for inspection, it's wise to consult with a reptile veterinarian or an experienced breeder. They can provide a professional assessment and guide you through the process safely.
An expert can also offer advice on the care and breeding of bearded dragons, ensuring that you're providing the best environment for your pet, regardless of their sex.
Summary
Determining the sex of your bearded dragon involves a combination of physical examination and behavioral observation. Look for hemipenal bulges, femoral pores, head and tail structure, and breeding behaviors as key indicators. Remember that age and sexual maturity are important factors, and when in doubt, seek expert advice. Knowing whether your bearded dragon is male or female is essential for proper care and, if desired, successful breeding.
FAQ Section
Q: At what age can you tell the sex of a bearded dragon? A: You can typically start to tell the sex of a bearded dragon when they reach sexual maturity, around 8 to 12 months of age. Before this, it can be difficult to distinguish males from females.
Q: Can you determine the sex of a bearded dragon without handling them? A: While some physical characteristics like head shape and tail thickness can be observed without handling, a more accurate determination often requires a closer inspection of the vent area for hemipenal bulges or femoral pores, which involves handling.
Q: Is it harmful to check a bearded dragon's hemipenal bulges? A: Checking for hemipenal bulges is not harmful if done gently and correctly. However, improper handling can cause stress or injury to the bearded dragon. If you're unsure how to perform this check, it's best to consult with a professional.




